08. Project Quality Managament
In continuing with the nine knowledge areas, the turn comes for project quality management. It is very important to understand the importance of project quality management for information technology products and services because this will help in giving a better output which means, satisfied customers and stakeholders/sponsors. It is very important to give outputs qualified for IT development teams because it sometimes may lead to fatal errors, like the case were in 1986, two hospital patients died after receiving fatal doses of radiation from a Therac 25 machine after a software problem caused the machine to ignore calibration data.
Quality in a project may be defined as "the project’s processes and products meet written specifications or more simple saying: "a product can be used as it was intended". For a more technical definition, we may refer to the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) which defines quality as “the degree to which a set of inherent characteristics fulfills requirements” (ISO9000:2000)
IN project quality management, there exists three processes:
1 - Quality planning: identifying which quality standards are relevant to the project and how to satisfy them.
2 - Quality assurance: periodically evaluating overall project performance to ensure the project will satisfy the relevant quality standards.
3 - Quality control: monitoring specific project results to ensure that they comply with the relevant quality standards.
Briefly now we are going to explain what happens on each of the phases.
Quality Planing
In this process, the project team strives to anticipate situations and prepare actions to bring about the desired outcome. It is important in this stage to prevent errors by selecting the best and proper materials, training and indoctrinating people in quality and by planning processes and estimating their outcomes.
Quality is part of all members in a team, that is, they have to consider quality but the main responsible for the quality in a project, is the project manager. Beside this, some organizations may help in understanding quality better. An example is ISO which was meant above.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance includes all the activities related to satisfying the relevant quality standards for a project. In this process it is important for companies to focus on continuous quality improvements. Benchmarking is a way that help in generating ideas for quality improvements by comparing specific practices or product characteristics to those of other organizations. So the important point here is: quality is not just a step in project management but it follows the project throughout its life.
Quality Control
And lastly, quality control. After the team tries all the best for the quality it is important also to have the quality control process. Outputs of quality control include:
- Acceptance decisions if expectations are met.
- Rework if is needed to change anything.
- Process adjustments.
Different tools of quality management include for performing quality control includes: Cause-and-effect diagrams (also known as fishbone or Ishikawa diagrams as shown in the picture), quality control charts, the seven run rule, run charts, scatter diagram, histogram, Pareto chart, Pareto analysis or even flowcharts.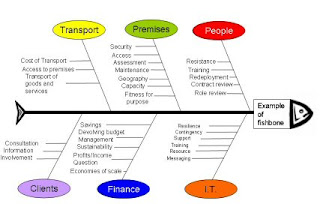
Another very important term that we focus in this chapter is "Six Sigma". Six Sigma is “a comprehensive and flexible system for achieving, sustaining, and maximizing business success. Six Sigma is uniquely driven by close understanding of customer needs, disciplined use of facts, data, and statistical analysis, and diligent attention to managing, improving, and reinventing business processes.” The main goal of it is; improve quality of services or products by reducing costs.
The last issue that we have to be aware in this step is testing. Many IT professionals think that testing should be done in the last phases of the project, when it is almost being released but the fact show the vice versa. It is important that testing is done in each phase of project completion and all errors detected should be fixed promptly, without any delay. An example of testing during the life cycle of a program development is shown for illustration purpose.

Quality in a project may be defined as "the project’s processes and products meet written specifications or more simple saying: "a product can be used as it was intended". For a more technical definition, we may refer to the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) which defines quality as “the degree to which a set of inherent characteristics fulfills requirements” (ISO9000:2000)
IN project quality management, there exists three processes:
1 - Quality planning: identifying which quality standards are relevant to the project and how to satisfy them.
2 - Quality assurance: periodically evaluating overall project performance to ensure the project will satisfy the relevant quality standards.
3 - Quality control: monitoring specific project results to ensure that they comply with the relevant quality standards.
Briefly now we are going to explain what happens on each of the phases.
Quality Planing
In this process, the project team strives to anticipate situations and prepare actions to bring about the desired outcome. It is important in this stage to prevent errors by selecting the best and proper materials, training and indoctrinating people in quality and by planning processes and estimating their outcomes.
Quality is part of all members in a team, that is, they have to consider quality but the main responsible for the quality in a project, is the project manager. Beside this, some organizations may help in understanding quality better. An example is ISO which was meant above.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance includes all the activities related to satisfying the relevant quality standards for a project. In this process it is important for companies to focus on continuous quality improvements. Benchmarking is a way that help in generating ideas for quality improvements by comparing specific practices or product characteristics to those of other organizations. So the important point here is: quality is not just a step in project management but it follows the project throughout its life.
Quality Control
And lastly, quality control. After the team tries all the best for the quality it is important also to have the quality control process. Outputs of quality control include:
- Acceptance decisions if expectations are met.
- Rework if is needed to change anything.
- Process adjustments.
Different tools of quality management include for performing quality control includes: Cause-and-effect diagrams (also known as fishbone or Ishikawa diagrams as shown in the picture), quality control charts, the seven run rule, run charts, scatter diagram, histogram, Pareto chart, Pareto analysis or even flowcharts.

Another very important term that we focus in this chapter is "Six Sigma". Six Sigma is “a comprehensive and flexible system for achieving, sustaining, and maximizing business success. Six Sigma is uniquely driven by close understanding of customer needs, disciplined use of facts, data, and statistical analysis, and diligent attention to managing, improving, and reinventing business processes.” The main goal of it is; improve quality of services or products by reducing costs.
The last issue that we have to be aware in this step is testing. Many IT professionals think that testing should be done in the last phases of the project, when it is almost being released but the fact show the vice versa. It is important that testing is done in each phase of project completion and all errors detected should be fixed promptly, without any delay. An example of testing during the life cycle of a program development is shown for illustration purpose.



Comments
Top Project Management consulting firm in the USA